Active Directory Certificate Service (AD CS) provides a number of customizable services related to public key infrastructures and certificates used in software security systems. It is comprised of components such as certificate authorities, CA web enrollment, online responder, and network device enrollment service.
It allows you to encrypt data files, encrypt remote communications, secure email messages, secure logons, secure servers, secure wireless communications, and protect all data from tampering. The AD CS can run in both corporate network and outside the corporate network. It can be integrated with AD DS to provide automated certificate enrollment.
AD CS deployments are hierarchical in nature and form a chain of trust from lowest to
top most point of a hierarchy. AD CS supports two CA types:
- Standalone CA: This CA runs on standalone servers and is not necessarily integrated with AD DS. It is often used as internal root CAs and can be taken offline for security purposes after being used to generate certificates for subordinate CAs.
- Enterprise CA: This CA is integrated with AD DS and is installed usually on member servers. They are used to issue CAs that are subordinate to another CAs in a hierarchy. They however, provide certificates to end users and endpoint devices. These CAs are usually online all the times.
Install AD CS as a Standalone Root CA
- Click Start-> Administrative Tools->Server Manager-> Roles Summary-> Add Roles
- Click Next on the first page of the Add Roles Wizard that appears.
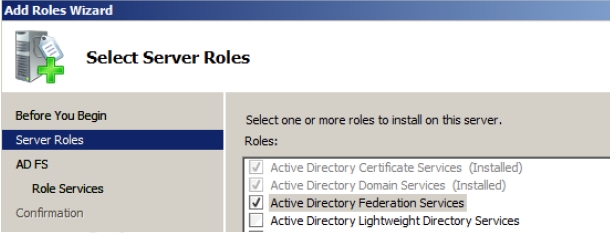
- Select Active Directory Certificate Services and then click Next on the Select Server Roles page that appears.
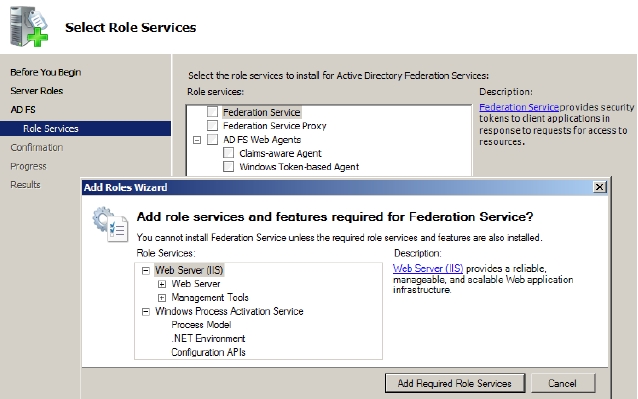
- Select Certification Authority on the Select Role Services page and click Next. Because this is a root CA you need not assign other services and roles to it, as shown in Figure 7-1:
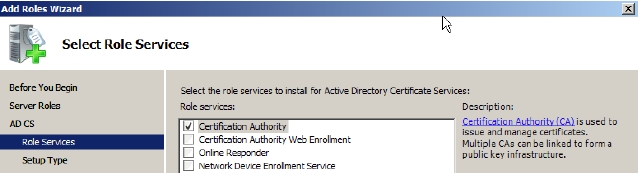
Figure 7-1 - Select Standalone on the Specify Setup Type page that appears and click Next.
- Select Root CA on the Specify CA Type page that appears and click Next.
- Select Create a new private key radio button on the Set Up Private Key and then select Next.You need to create a new private key because you are creating a new root CA. If you are reinstalling a CA due to some reason then you can select the existing key option.The Configure Cryptography for CA page appears with a number of cryptography options to configure.
CSP are the engines that MS crypto API uses to generate key pair for the root CA CSP can be software or hardware based. For example The RSA#Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider CSP is software based and RSA#Microsoft Smart Card Storage Provider CSP is hardware based.
- Select the suggested cryptographic service provider from the Select the cryptographic service provider (CSP) dropdown.The Key character length field allows you to select the length of the cryptography keys in pair. Before selecting the key length, you must know that longer the key length the more processing time the server will take
- Select the appropriate key length from the Key character length field.The Hash algorithms are used to produce and assign hash value on the keys in pair. The hash value on key pairs ensures that the no tempering has been done with the data in the transit.
- Select the SHA1 hash algorithm from the Select the hash algorithm for signing certificates issued by this CA dropdown to ensure the backward-compatibility with old versions.The Use strong private key protection features provided by the CSP option further ensures the protection of the root CA. This is because if this option is selected the CA will require only administrative access to work with, as shown in Figure 7-2.
- Keep Use strong private key protection features provided by the CSP option deselected for this example and click Next
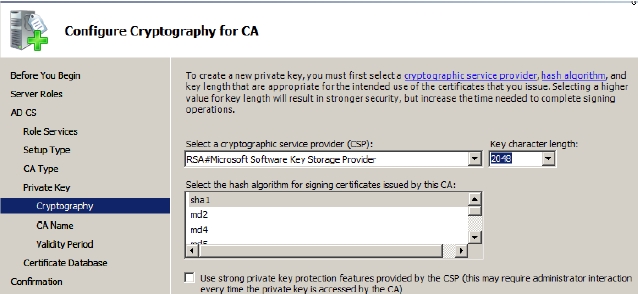
Figure 7-2 - Modify the Common name of the CA in the Common name for this CA field and leave the Distinguished name suffix field as is. For this example modify the name to Inscription-Root-CA, as shown in Figure 7-3.The common name that you specify here will be embedded in each subordinate certificate issued by the name.
- Click Next.
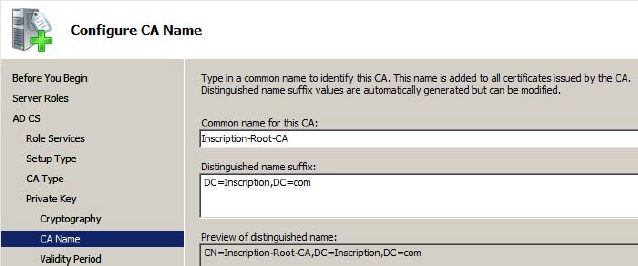
Figure 7-3 - Modify the validity period of the CA in the Select validity period for the certificate generated for this CA fields if required on the Set Validity Period page, as shown in Figure 7-4 and then click Next.
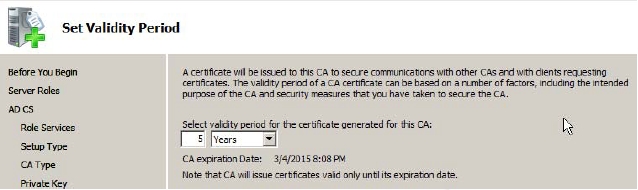
Figure 7-4 - Accept the default values for the certification database or modify them if required on the Configure Certificate Database page, as shown in Figure 7-5 and click Next.
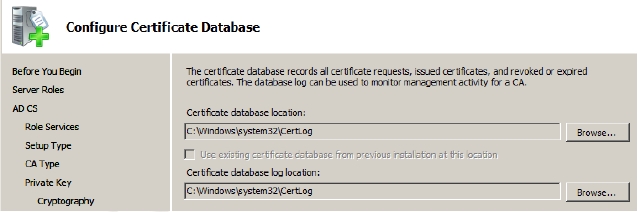
Figure 7-5 - Click Install on the Confirm Installations Selections pageThe installation process starts and you will now never be able to change the name of the server unless you uninstall AD CS first.